What Was the First Abstract Artwork?
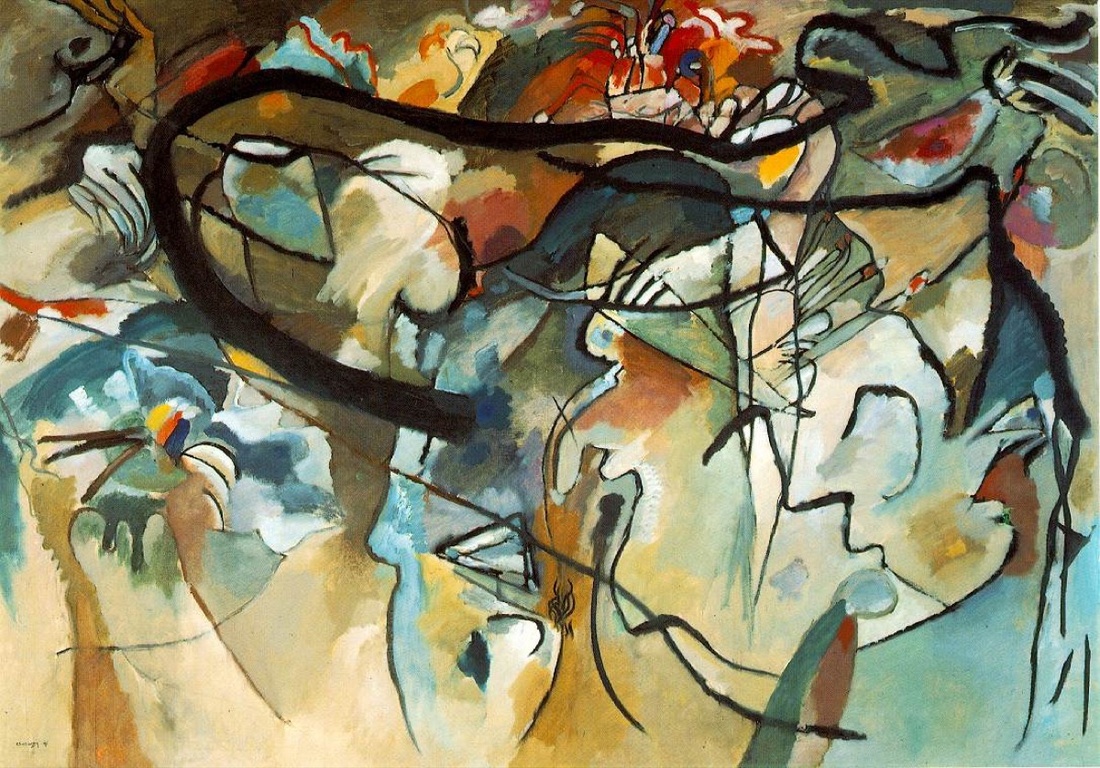 Wassily Kandinsky, Composition V, 1911. Image via Wikimedia Commons.
Wassily Kandinsky, Composition V, 1911. Image via Wikimedia Commons.
Who made the first Western abstract painting? That was the question that Wassily Kandinsky’s widow, accompanied by a team of researchers, set out to answer in 1946. Her late husband, a Russian painter who was among the pioneers of abstraction in the early 1910s, had himself been personally invested in the answer.
In 1935, Kandinsky had penned a letter to his gallerist in New York to insist on his preeminence. “Indeed,” he wrote of a 1911 work, “it’s the world’s first ever abstract picture, because back then not one single painter was painting in an abstract style. A ‘historic painting’, in other words.”
Kandinsky wasn’t the only artist interested in preserving his legacy. He and several early abstract painters—including Robert Delaunay, Mikhail Larionov, Natalia Goncharova, and Kazimir Malevich—backdated their works, in some cases several years before they were actually completed.
This artistic jostling reflects a focus on invention as an individual act, notes curator Leah Dickerman in an essay for MoMA’s 2012 show “Inventing Abstraction, 1910-1025: How a Radical Idea Changed Modern Art.” But, as she goes on to say, that approach is in some ways misguided. Rather than the work of a solitary genius, abstraction “was an invention with multiple first steps, multiple creators, multiple heralds, and multiple rationales.”
At the turn of the 20th century, the world was becoming increasingly connected. Steamships, cars, and trains facilitated international travel, while telephones, telegraphs, and radios allowed for conversations between people on opposite ends of the globe.
Within the art world specifically, journals sprang up in droves; in Paris alone, some 200 reviews of art and culture appeared in the decade leading up to World War I. Subscribers were scattered across Europe and America, allowing a wide swath of creatives to stay abreast of the latest developments in art. And this period also saw the beginning of a traveling exhibition culture, led by the Italian Futurists.
“Historians talk about ‘conditions of possibility,’” Masha Chlenova, a curator who worked with Dickerman on “Inventing Abstraction,” told Artsy. “For example, photography was also invented by three people at the same time. Daguerre just happened to be the best at marketing and patenting.”
Similarly, while Kandinsky is today hailed as the father of abstract painting, he was by no means the only player in the development of non-representational painting. His work Komposition V did, admittedly, jumpstart public interest in abstract painting. Exhibited in Munich in December 1911, this monumental work was just barely representational.
It was the first such work to be put on display, and “for some artists and intellectuals, abstraction not only began to seem plausible, but also took on the character of an imperative,” Dickerman writes.
Kandinsky had been thinking about abstract art for years beforehand. His manifesto On the Spiritual in Art, which appeared as a draft in 1909 and was published the same month as Komposition V went on display, laid out the tenets of abstraction. But it would still be several years before Kandinsky would finally break free from recognizable forms in his art. As Chlenova put it, “he theorized abstraction before he made painting.”
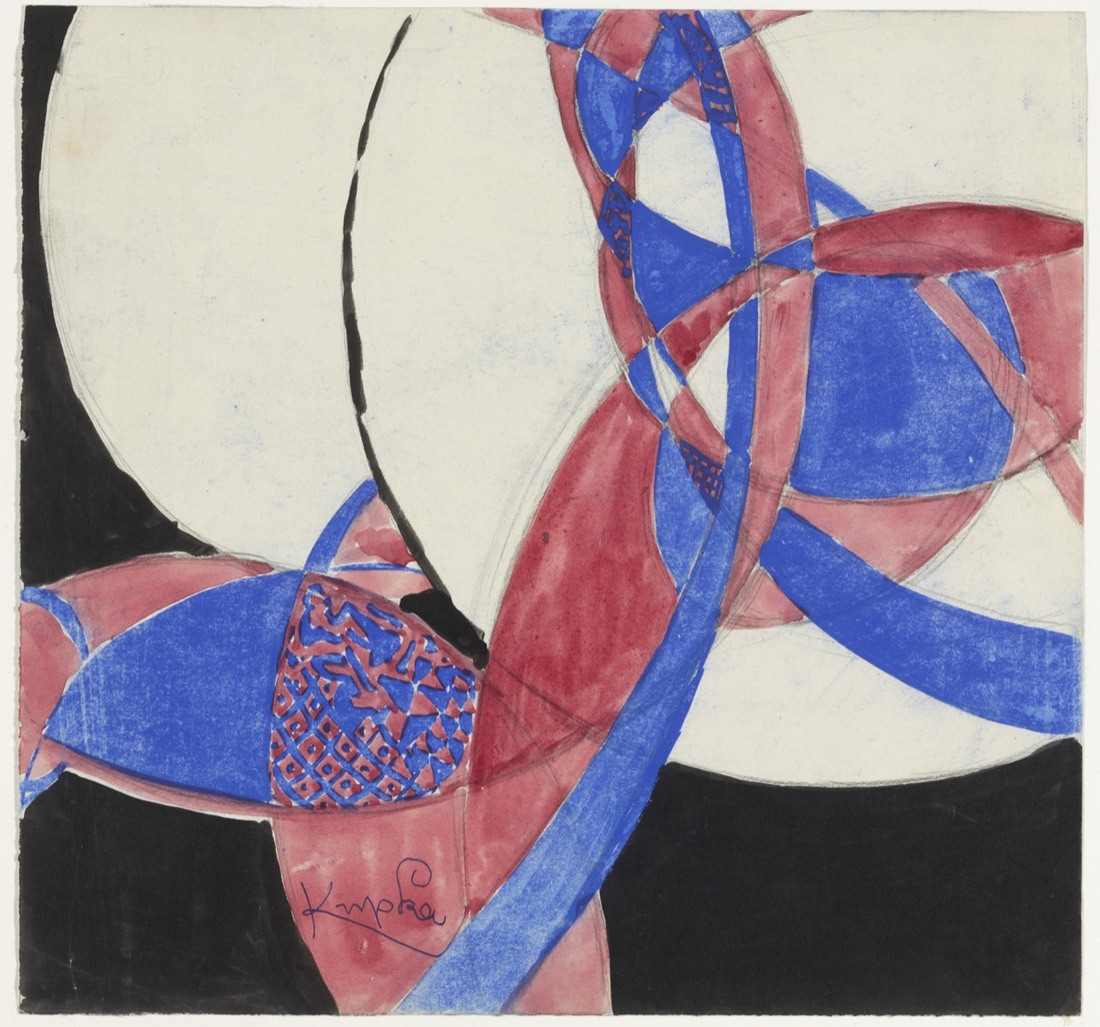 František Kupka, Amorpha: Fugue in Two Colors, 1912. Courtesy of The Museum of Modern Art, NY. © 2017 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / ADAGP, Paris.
František Kupka, Amorpha: Fugue in Two Colors, 1912. Courtesy of The Museum of Modern Art, NY. © 2017 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York / ADAGP, Paris.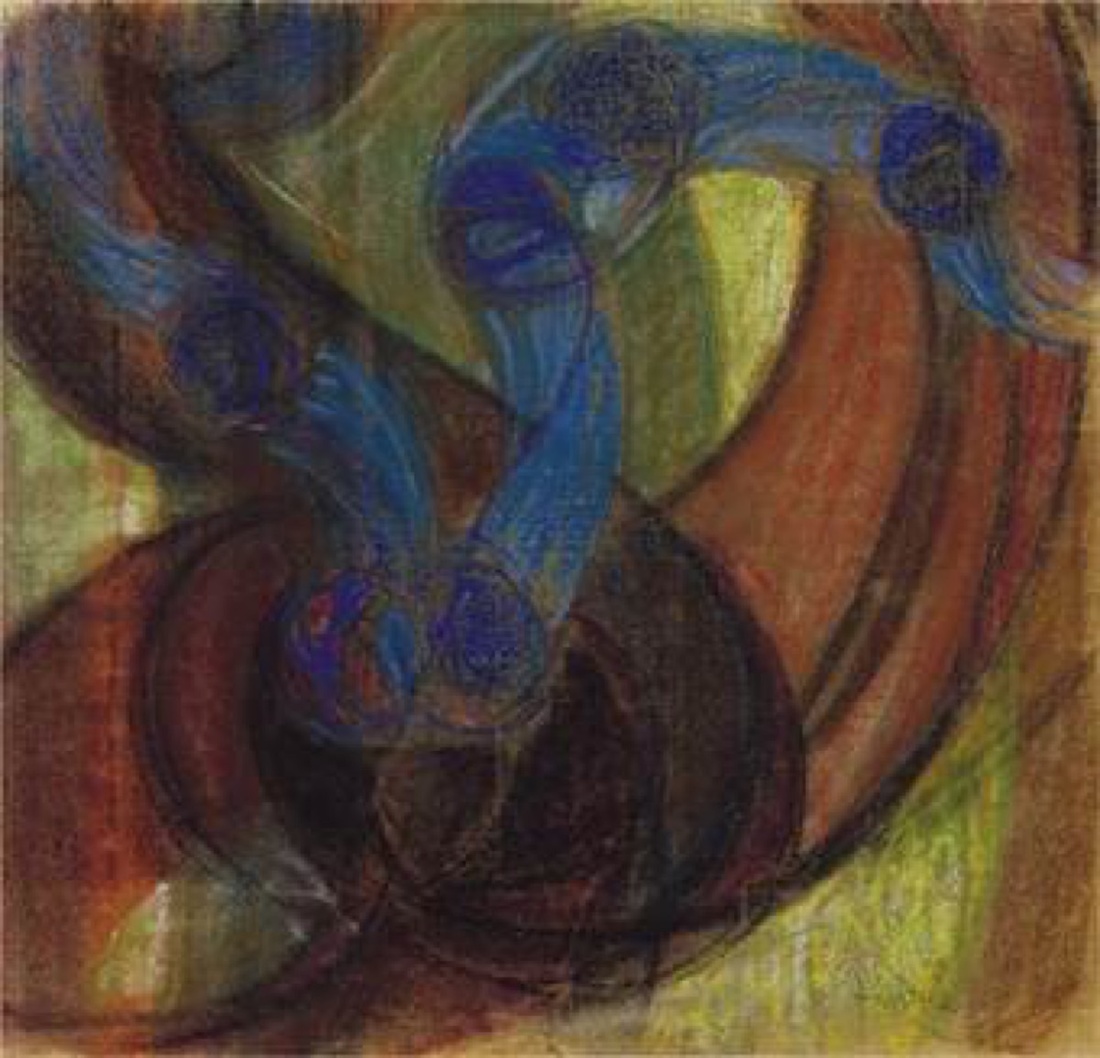 František Kupka Study for Amorpha, Warm Chromatic and for Fugue in two colors; Study for The Fugue, 1910–11. The Solomon R. Guggenheim Foundation Peggy Guggenheim Collection, Venice, 1976. © 2017 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York/ADAGP, Paris.
František Kupka Study for Amorpha, Warm Chromatic and for Fugue in two colors; Study for The Fugue, 1910–11. The Solomon R. Guggenheim Foundation Peggy Guggenheim Collection, Venice, 1976. © 2017 Artists Rights Society (ARS), New York/ADAGP, Paris.
Dickerman references Czech-born artist František Kupka as the first to display works that were a complete break from representational painting. His compositions Amorpha, Chromatique chaude and Amorpha, Fugue à deux couleurs were shown at the Salon d’Automne in Paris in October 1912, filmed for the newsreels, and then broadcast across Europe and America.
Dickerman believes that Kupka’s willingness to publicly defy convention was related to his personal history. Although he grew up in Prague and Vienna and started out as a Symbolist, he later moved to Paris and developed close ties with the city’s avant-garde—which, as Dickerman notes, granted “him an insider/outsider status that seems particularly fertile for paradigm-shifting thought.”
But further complicating the question of “first” is that it can be difficult to determine the threshold of abstraction. When, precisely, does a work go from “abstracted” to “abstraction”?
French avant-garde artist Francis Picabia, for example, is sometimes credited with the first abstract painting. His watercolor Caoutchouc (Rubber) was completed in 1909, which would predate even Kandinsky’s theories on abstraction. But other academics have pushed back, noting that the work still retains some semblance of form, reminiscent of a bouquet of flowers.
For “Inventing Abstraction,” Chlenova said she and Dickerman began by establishing clear criteria for what they considered abstract work. “Our main criterion was the artist’s own position and their statements that they’re doing something abstract,” she said. “The terminology is a slightly different question because the word ‘abstract’ would not necessarily be used. But there was a very clear awareness from the artists that were sensitive to what was happening.”
 Hilma af Klint, The Large Figure Paintings, No. 5, Group III, 1907. Image via Wikimedia Commons.
Hilma af Klint, The Large Figure Paintings, No. 5, Group III, 1907. Image via Wikimedia Commons. Hilma af Klint, Svanen (The Swan) No. 17, Group IX/SUW, The SUW/UW Series, 1914-1915. Image via Wikimedia Commons.
Hilma af Klint, Svanen (The Swan) No. 17, Group IX/SUW, The SUW/UW Series, 1914-1915. Image via Wikimedia Commons.
This is why, she explained, Swedish artist Hilma af Klint was not represented in the MoMA exhibition. Since 2013, when Moderna Museetheld the first-ever retrospective of her work, af Klint’s oeuvre has received renewed attention from the public. Known in her lifetime as a landscape painter and portraitist, it was revealed decades after her death that she had also been experimenting with abstraction. As early as 1906, af Klint had been painting colorful works full of organic shapes, spirals, and curlicues.
This date places her several years before Kandinsky even theorized abstraction, let alone acted on his ideas. But af Klint’s works sprang from her interest in the occult—during the 1890s, she started organizing seances with four artist friends where they practiced automatic drawing and writing.
Later, when she began her largest body of non-representational paintings, she claimed that spiritual forces were directing her hand. And for an artist to be included in “Inventing Abstraction,” Chlenova explained, they had to “formulate their practice as a conscious rejection of any reference to the outside world.”
Others disagreed with this reading, arguing that a mystical approach should not negate her contribution to developing abstraction. “‘Spiritual’ is still a very dirty word in the art world,” curator Maurice Tuchman toldthe New York Times in 2013. “When the prejudice against the idea of the spiritual life in af Klint’s work is overcome, which will require scholarship, then perhaps she will really take hold in the broader conversation.”
But there’s no disagreement that the invention of Western abstraction revolutionized art production in the 20th century, nor that it was predated by centuries of abstracted forms and patterns in non-Western traditions.
“One can treat abstraction a little bit more abstractly, if you will,” Chlenova laughed, “without ultimately being too concerned about who was first.”
—Abigail Cain


No comments:
Post a Comment